Introduction
The Development Of Mineral Deposits Homework Help is a critical topic in geology, mining engineering, and environmental science. Understanding how mineral deposits form and evolve over time is essential for resource management, mining, and economic development. This blog provides a comprehensive guide to the development of mineral deposits, their formation processes, mining techniques, and environmental considerations. Whether you’re a student needing homework assistance or a professional looking for insights, this guide will help you grasp key concepts.
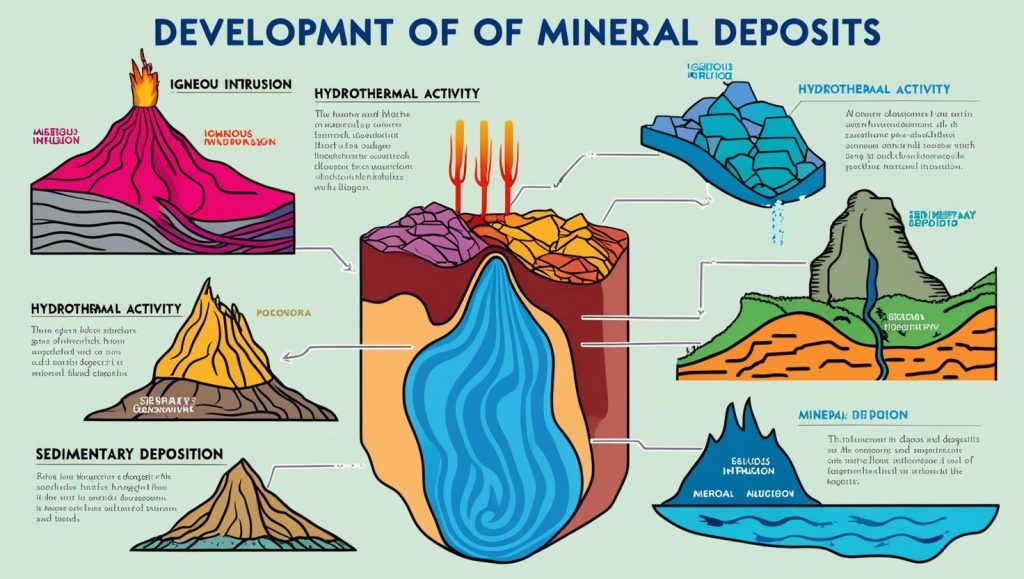
What Are Mineral Deposits?
Mineral deposits are naturally occurring concentrations of minerals that can be extracted economically. They form through geological processes over millions of years and serve as vital resources for various industries. The study of mineral deposits involves aspects of geology, geochemistry, and geophysics to determine their commercial viability.
Types of Mineral Deposits
Mineral deposits are classified based on their formation process and economic value. The primary categories include:
- Magmatic Deposits: Formed from cooling magma that solidifies and concentrates minerals.
- Hydrothermal Deposits: Created when mineral-rich hot water circulates through rock formations, depositing minerals.
- Sedimentary Deposits: Result from the accumulation of mineral particles transported by water, wind, or ice.
- Placer Deposits: Occur when minerals are concentrated in riverbeds or beach sands due to erosion.
- Metamorphic Deposits: Form under heat and pressure conditions that cause mineral transformations.
Formation Processes of Mineral Deposits
The formation of mineral deposits involves several geological processes:
1. Magmatic Differentiation
As magma cools, minerals crystallize at different temperatures, causing heavier minerals to settle at the bottom of magma chambers. This process forms layered deposits of valuable ores like chromite, magnetite, and platinum-group metals.
2. Hydrothermal Activity
Hydrothermal fluids, rich in dissolved minerals, migrate through rock fractures and deposit valuable metals like gold, silver, and copper when the temperature and pressure conditions change.
3. Sedimentary Processes
Minerals settle out of water bodies over time, forming layers of valuable resources such as iron ore, limestone, and phosphates. Evaporation of mineral-rich water can also create deposits like salt and gypsum.
4. Weathering and Erosion
Weathering breaks down rocks, releasing minerals into soil and water systems. These minerals may accumulate in rivers, forming placer deposits of gold and diamonds.
5. Metamorphic Reactions
Extreme heat and pressure can alter existing minerals, leading to the formation of valuable resources such as graphite, marble, and garnet.
Exploration and Mining Techniques
Once a mineral deposit is identified, exploration and mining techniques are employed to extract the resource efficiently. The key stages include:
1. Geological Surveys
Geologists conduct surveys using satellite imagery, geochemical analysis, and field mapping to locate potential deposits.
2. Drilling and Sampling
Drilling methods such as core drilling and rotary drilling help obtain underground samples for laboratory analysis.
3. Mining Methods
Depending on the deposit type and depth, different mining methods are employed:
- Surface Mining: Includes open-pit mining and strip mining for shallow deposits.
- Underground Mining: Used for deep-seated mineral deposits, employing shafts and tunnels.
- Placer Mining: Involves panning, sluicing, and dredging in riverbeds.
Environmental and Economic Considerations
Mining has significant environmental and economic implications. Sustainable practices are essential to minimize the impact on ecosystems and communities.
Environmental Impact
- Deforestation and Land Degradation: Large-scale mining operations clear vast land areas, affecting biodiversity.
- Water Pollution: Chemical runoff from mining activities can contaminate water sources.
- Air Pollution: Dust and emissions from mining contribute to air pollution.
Economic Benefits
- Job Creation: The mining industry provides employment opportunities worldwide.
- Economic Growth: Mineral exports contribute to national economies, especially in resource-rich countries.
- Technological Advancement: Mining drives innovation in engineering and environmental management.
The Future of Mineral Development
As global demand for minerals increases, sustainable mining practices and technological advancements will shape the industry’s future. Innovations such as automation, AI-driven exploration, and eco-friendly mining techniques will play a crucial role in ensuring long-term resource availability.
Conclusion
Understanding the Development Of Mineral Deposits Homework Help provides valuable insights into geology, mining, and sustainability. Mineral deposits play a vital role in global economies and industries, making their study essential for students and professionals alike. With advancements in mining technology and sustainable practices, the future of mineral development remains promising.
For more information on mineral deposits and mining processes, visit US Geological Survey (USGS) or International Council on Mining & Metals (ICMM).


